Category: Constitution of India & Polity
Right to Information Act 2005 (सूचना का अधिकार अधिनियम)
Right to Information Act 2005 mandates timely response to citizen requests for government information. It empowers the citizens for quick search of information on the details of first Appellate Authorities,…
(Practice Quiz) NCERT Based MCQs- Class XII Politics in India Since Independence
Conceptual understanding of all the topics is the most important part of preparation for an examination. CBSE Curriculum based Objective Questions from Class-VI to XII provide an excellent option to…
(Practice Quiz) General Studies MCQs based on NCERT- Indian Polity
Conceptual understanding of all the topics is the most important part of preparation for an examination. CBSE Curriculum based Objective Questions from Class-VI to XII provide an excellent option to…
(Practice Quiz) NCERT Based MCQs- X Civics
Conceptual understanding of all the topics is the most important part of preparation for an examination. CBSE Curriculum based Objective Questions from Class-VI to XII provide an excellent option to…
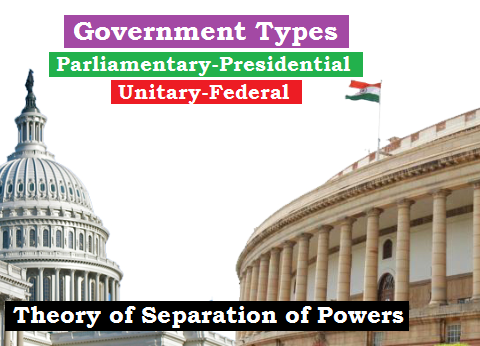
Government Types: Parliamentary- Presidential, Unitary- Federal and Theory of Separation of Powers (शासन के प्रकार:संसदीय-अध्यक्षात्मक एवं एकात्म-संघात्मक और शक्ति पृथकरण का सिद्धांत)
Government Types: Parliamentary Vs Presidential Features Parliamentary Govt Presidential Govt 1. Dual executive (Prime Minister is the defacto and President is the dejure Executives) 1. Single executive 2. Majority party…
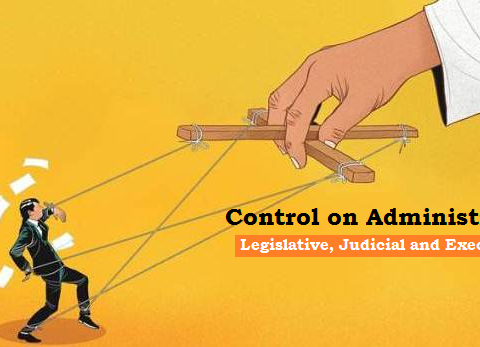
Control on Administration in India: Parliamentary, Executive and Judicial (भारत मे प्रशासन पर नियंत्रण:संसदीय, कार्यपालिक एवं न्यायिक)
Administration is run by the bureaucracy- the officers appointed in different departments. They follow the rules and procedures framed by the Legislature and the Executive. They can’t work and act…
Relation between Center and States: Financial
The Constitution of India, being federal in structure, in Part XI divides powers- legislative, administrative, financial- between the Center and the States.The Center- State relations can be divided under three…
Relation between Center and States: Executive (Administrative)
The Constitution of India, being federal in structure, in Part XI divides powers- legislative, administrative, financial- between the Center and the States.The Center- State relations can be divided under three…
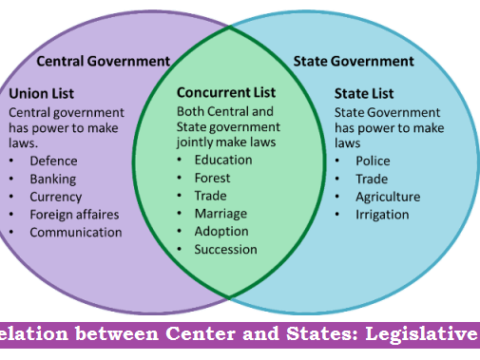
Relation between Center and States: Legislative
The Constitution of India, being federal in structure, in Part XI divides powers- legislative, administrative, financial- between the Center and the States.The Centre- State relations can be divided under three…
Constitutional Development of India (1773-1950)
Background Here are some of the important Regulations and Acts: Centralization of Power 1. Regulating Act (1773): First step to control and regulate Company affairs 2. Pitt’s India Act (1784):…

 Home
Home Syllabus
Syllabus Contact Us
Contact Us