Category: Paper-VI
(Topic-Wise Mains Papers) Paper-VI: Social Aspect of Chhattisgarh (छत्तीसगढ़ का सामाजिक परिदृश्य)
Paper- VI (General Studies- IV: Philosophy and Sociology) (200 Marks) Part 03: Social Aspect of Chhattisgarh Tribal social organization: Marriage, Family, Clan, youth dormitories. 2021 Write an essay on the…
(Topic-Wise Mains Papers) Paper-VI: Sociology (समाजशास्त्र)
Paper- VI (General Studies- IV: Philosophy and Sociology) (200 Marks) Part 02: Sociology (50 Marks) Sociology: Meaning, scope and nature; importance of its study; relation with other social sciences. 2023…
(Topic-Wise Mains Papers) Paper-VI: Philosophy (दर्शनशास्त्र)
Paper- VI (General Studies- IV: Philosophy and Sociology) Part 01: Philosophy Indian Philosophy: Nature of Philosophy, its relation between religion and culture, difference between Indian and western Philosophy 2023 1. What…
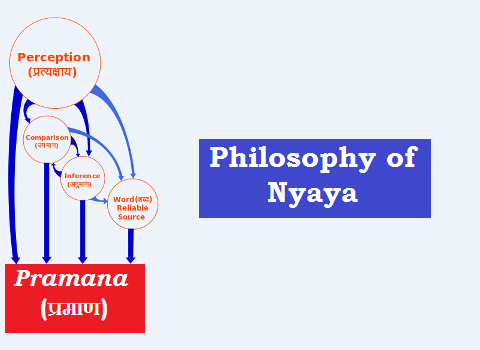
Philosophy of Nyaya (न्याय दर्शन): Prama, Aprama, Asatkaryavada (प्रमा, अप्रमा, असत्कार्यवाद)
Nyaya means right thinking with proper arguments and valid reasoning. Therefore, it is also known as Tarkashastra (the science of reasoning). Nyaya School of thought is adhered to atomistic pluralism…
Philosophy of Yoga (योग दर्शन): Ashtanga Yoga (अष्टांग योग)
The word ‘Yoga’ literally means ‘union’, i.e., spiritual union of the individual soul with the universal soul and is used in this sense in the Vedanta. According to Patanjali, who…
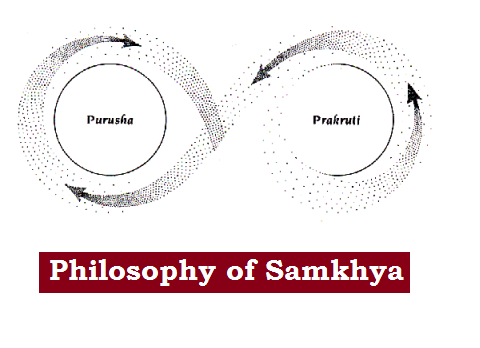
Philosophy of Samkhya (सांख्य दर्शन): Satkaryavada, nature of Prakriti and Purusha, Vikasavada (सत्कार्यवाद, प्रकृति एवं पुरुष का स्वरूप तथा विकासवाद)
The Samkhya Philosophy is regarded as dualistic realism; dualistic because it holds the doctrine of two ultimate realities: Prakriti (non-self) and Purusa (self). It is realism because it views that…
Philosophy of Buddha (बोद्ध दर्शन): Pratityasamutpada, Ashtanga Marg, Anatmavada, Kshanikvada (प्रतित्यसमुत्पाद, अष्टांग मार्ग, अनात्मवाद, क्षणिकवाद)
Buddhist Philosophy is one of the Nastika or Heterodox Schools of Indian philosophy. Most Buddhist traditions emphasize on the attainment of Nirvana-ending the cycle of death and rebirth by conquering…
Philosophy of Jain (जैन दर्शन): Nature of Jiva, Anekantvada, Syadavada, Panchamahavrata (जीव का स्वरूप, अनेकांतवाद, स्याद्वाद, पंचमहाव्रत)
Read about Jainism here. Jain= jina meaning conqueror Meaning: one who has conquered one’s inner enemies (passions) Jain Philosophy is one of the Nastika or Heterodox Schools of Indian philosophy. Jain…
Philosophy of Charvaka (चावार्क दर्शन): Epistemology, Metaphysics, Hedonism (ज्ञानमीमांसा, तत्वमीमांसा, सुखवाद)
Charvaka Philosophy is one of the Nastika or Heterodox Schools of Indian philosophy. It holds direct perception, empiricism, and conditional inference as proper sources of knowledge, embraces philosophical skepticism and…
Philosophy of Gita (गीता दर्शन): Sthitpragya, Swadharma, Karmayoga (स्थितप्रज्ञ, स्वधर्म, कर्मयोग)
Bhagavat Gita= Bhagavad: Lord; Gita: song Meaning: Song of the Lord Bhagavat Gita is the literature written in poetic form is a part of the epic Mahabharata (under Bhishma Parva) complied around 200…

 Home
Home Syllabus
Syllabus Contact Us
Contact Us