Category: CGPSC Mains
Right to Information Act 2005 (सूचना का अधिकार अधिनियम)
Right to Information Act 2005 mandates timely response to citizen requests for government information. It empowers the citizens for quick search of information on the details of first Appellate Authorities,…
Important Schemes of Chhattisgarh Government (छत्तीसगढ़ शासन की योजनाएँ) March 2024
As included in the election manifesto (‘Modi ki Guarantee’) for the Vidhan Sabha Elections, the newly formed government launched many schemes to fulfil the promises made under ‘Modi ki Guarantee’….
State Finance and Budgetary Policy: Budget 2024-25 (राज्य की वित्त एवं बजटीय नीति: बजट 2024-25)
For Basics of State Finance and Budget, please go through Fiscal Policy: Budget, Fiscal Deficit, Public Debt. This is the first budget presented by newly formed government as “Amritkaal ke…
Issues related to Girls’ Education (बालिकाओं की शिक्षा से संबन्धित मुद्दे)
Girls’ education is a strategic development priority. It is an important tool that enables women and girls to participate in decisions that affect their lives and in improving their social…
(Vedic Mathematics) (वैदिक गणित) Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division and Vinculum (जोड़ना, घटाना, गुना, भाग तथा विंकुलम)
Vedic Sutras 1. Ekadhiken Purven (एकाधिकेन पूर्वेण): Increasing (एकाधिक) a number to the digit which comes before (पूर्व) For example, Edadhik of 12 It is represented by a dot on…
Topic Wise Analysis | CGPSC Mains 2020
Here is our topic-wise analysis of recently conducted CGPSC Mains 2020. The topics from the syllabus which were asked directly or indirectly are also mentioned. About 42% questions were directly…
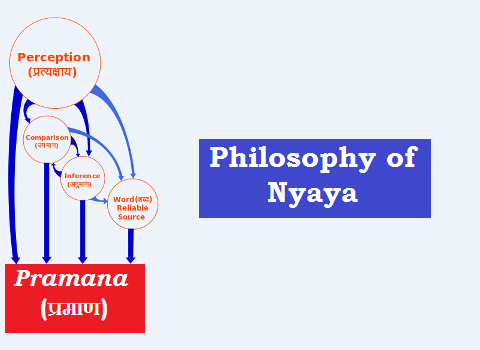
Philosophy of Nyaya (न्याय दर्शन): Prama, Aprama, Asatkaryavada (प्रमा, अप्रमा, असत्कार्यवाद)
Nyaya means right thinking with proper arguments and valid reasoning. Therefore, it is also known as Tarkashastra (the science of reasoning). Nyaya School of thought is adhered to atomistic pluralism…
Philosophy of Yoga (योग दर्शन): Ashtanga Yoga (अष्टांग योग)
The word ‘Yoga’ literally means ‘union’, i.e., spiritual union of the individual soul with the universal soul and is used in this sense in the Vedanta. According to Patanjali, who…
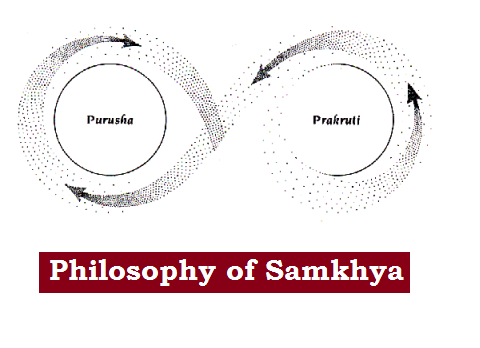
Philosophy of Samkhya (सांख्य दर्शन): Satkaryavada, nature of Prakriti and Purusha, Vikasavada (सत्कार्यवाद, प्रकृति एवं पुरुष का स्वरूप तथा विकासवाद)
The Samkhya Philosophy is regarded as dualistic realism; dualistic because it holds the doctrine of two ultimate realities: Prakriti (non-self) and Purusa (self). It is realism because it views that…
Philosophy of Buddha (बोद्ध दर्शन): Pratityasamutpada, Ashtanga Marg, Anatmavada, Kshanikvada (प्रतित्यसमुत्पाद, अष्टांग मार्ग, अनात्मवाद, क्षणिकवाद)
Buddhist Philosophy is one of the Nastika or Heterodox Schools of Indian philosophy. Most Buddhist traditions emphasize on the attainment of Nirvana-ending the cycle of death and rebirth by conquering…

 Home
Home Syllabus
Syllabus Contact Us
Contact Us