
For Basics of State Finance and Budget, please go through Fiscal Policy: Budget, Fiscal Deficit, Public Debt.
Chhattisgarh Government has unveiled its ambitious Budget for the financial year 2025-26, reflecting a strong commitment to inclusive development, social welfare, and infrastructure growth. While the previous year’ budget laid a foundation for inclusive development, this year’s budget has presented the next step in that developmental journey.
While the budget of the previous year focused on the theme of GYAN (Gareeb, Yuva, Annadata & Nari), this year’s budget aims to drive progress in the State under the theme of GYAN ke liye GATI (Good Governance, Accelerating Infrastructure, Technology, Industrial Growth) to build on the progress made in this year and continue the journey with a rapid progress towards achieving our goals for 2030, as a part of Amrit Kaal Vision 2047.
Notably, this marks the Silver Jubilee Budget of the state, and as a tribute to former Prime Minister Shri Atal Bihari Vajpayee, the government has dedicated this year as Atal Nirman Varsh.
GATI Budget

1. G- Governance:
- Implementation of Next Generation Integrated Financial Management Information System to enhance efficiency, transparency and accountability in government financial operations
- Implementation of e-File system for online processing of files
- Development of Atal Monitoring Portal (Mukhyamantri Dashboard) which will provide a comprehensive dashboard to track the progress of government projects
- Upgradation of the online mineral management system – Khanij Online
- Establishment of Mukhyamantri Helpline to assist citizens with government services and schemes
- Use of GEM portal for public procurement
- Faceless and Paperless Registration of immovable property Sale-Purchase
- Mukhyamantri Governance Fellowship in collaboration with IIM & IIIT Raipur
2. A-Accelerating Infrastructure:
- Mukhyamantri Griha Pravesh Samman Vojna: 100 Crores
- 1000-seater auditorium at Bilaspur: 25 Crores
- Horticulture University: 170 Crores
- Allocation for Infrastructure development of ULBs: 750 Crores
- Development of Atal Smarak and Sangrahalaya: 40 Crores
- Development of Airports at Jagdalpur, Bilaspur and Ambikapur
- Establishment of New Fire Stations & Capacity Augmentation: 44 Crores
- Strengthening of Police Stations: 70 Crores
3. T – Technology:
- Computerization of courts: 37 Crores
- Dial 100/112 Services: 125 Crores
- Implementation of e-Dharti: 48 Crores
- Business Intelligence Unit at Commercial Tax Department: 41 Crores
- Establishment of State Data Center: 40 Crores
- Computerization of primary agriculture co-operative societies: 24 Crores
- Operation & Maintenance of Crime and Criminal Tracking Network System: 25 Crores
- Establishment of Digital Governance: 9 Crores
- Implementation of Vehicle Tracking Platform at Transport Department: 8 Crores
- Implementation of Statistical Analysis System for Collecting District GDP Data: 7 Crores
- Digital Crop Survey under national e-governance scheme: 40 Crores
- Operation & Maintenance of Statewide Area Network: 18 Crores
- Implementation of Bharat Net Program: 15 Crores
- Development of Urban Administration (ULBs) Integrated Dashboard: 10 Crores
4. I – Industrial Growth:
- Besides Core sectors, promotion of services sectors.
- Preference to Agniveers and surrendered Naxals in jobs.
- Implementation of Single Window System under BRAP – Business Reform Action Plan to promote Ease of Doing Business.
- Implementation of ERP Application at CSIDC.
- Implementation of Invest Chhattisgarh Program.
- Employment-Oriented Industrial Policy.
- Industry Budget 3 times of last year’s budget.
Chhattisgarh Budget Analysis (2025-26)
Budget Highlights:
- The Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) is estimated to be Rs 6,35,918 Crore which is 12.0% higher than 2024-25 (RE). It has increased substantially from 5,705 Crores in 2001-02.
- The Fiscal Deficit is estimated to be Rs 18,900 Crore which is 2.97% of GSDP. This is within the limit of 3% set in the FRBM Act.
- The Capital Expenditure is estimated to be Rs 26,341 Crore which 18% higher than 2024-25 (RE) and Capex to GSDP is 4.14% (3.93% in 2024-25 (RE)). Chhattisgarh is among the top states with high capex to GSDP ratio.
- Total revenue surplus estimated in the year is of Rs 2,804 Crores. Chhattisgarh is among the progressive states which maintain a revenue surplus status.
- As a result of positive efforts made to increase the revenue of the state, State’s own revenue is estimated to be increase by 11% over that of 2024-25 (RE) to Rs 76,000 crore in 2025-26.
| Head | 2024-25 (Revised-RE) | 2025-26 (Estimate-BE) |
| Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) | 5.68 Lakh Crore | 6.36 Lakh Crore 12.0% higher than 2024-25 (RE) |
| Net Expenditure | 1.52 Lakh Crore | 1.65 Lakh Crore 8.7% higher than 2024-25 (RE) |
| Capital Expenditure | 22.3k Crore | 26.3k Crore 18.0% increase over 2024-25 (RE) |
| Revenue Expenditure | 1.25 Lakh Crore | 1.38 Lakh Crore 11.0% increase over 2024-25 (RE) |
| Loans and Advances | 300 Crore | 463 Crore 54.3% higher than 2024-25 (RE) |
| Net Receipts | 1.52 Lakh Crore | 1.65 Lakh Crore 8.6% higher than 2024-25 (RE) |
| Capital Receipts | 30.8k Crore | 24.1k Crore 21.8% lower than 2024-25 (RE) |
| Revenue Receipts | 1.21 Lakh Crore | 1.41 Lakh Crore 16.3% increase over 2024-25 (RE) |
| Revenue Balance (-) Deficit | (-) Rs 7.2k Crore (-) 1.26% of GSDP | (+) Rs 2.8k Crore (+) 0.4% of GSDP |
| Fiscal Balance (-) Deficit | (-) Rs 29.3k Crore (-) 5.1% of GSDP | (-) Rs 22.9k Crore (-) 3.6% of GSDP* |
| Primary Balance (-) Deficit | (-) Rs 20.3k Crore (-) 3.58% of GSDP | (-) Rs 13.4k Crore (-) 2.1% of GSDP |
Source: Summary of the Budget 2024-25 | Main Budget 2024-25 | Press Note
*This includes provision of 4,000 Cr for Special Central Assistance for Capex. Net Fiscal Deficit after deducting SCA as per GoI Guidelines is 18,900 Cr, which is 2.97% of GSDP 2025-26.
Policy Highlights: New Initiatives with 10 New Schemes
- Mukhyamantri Mobile Tower Scheme to provide mobile tower connectivity in remote areas.
- Funds for Mukhyamantri Parivahan Yojana to provide Public Transport Services from Gram Panchayat to Block and District Level in areas where Public Transport is not available due to low density of Population.
- 500 new Co-operative Societies will be formed
- First time provision in the budget for procurement of Pulses and Oil seeds under Price Support Scheme (PSS) of Government of India.
- Rs. 500 Crores for Mukhyamantri Nagarotthan Yojana for DPR based development of Municipal Corporations.
- Establishment of National Institute of Fashion Technology in the state.
- 1st phase of Establishment of Sickle Cell Screening Center in all blocks of Chhattisgarh State.
- Survey for Interlinking of Mahanadi – Indravati and Sikasar – Kodar Rivers.
- Medi city will be established in Nava Raipur.
- Education City will be established in Nava Raipur.
- Establishment of National Institute of Urban Management in Nava Raipur.
- Budget provision to promote UPI (Digital payments) in all Gram Panchayats.
- Like National Security Guard (NSG), a dedicated Special Operation Group will be setup in State.
- Funds for developing Iconic Destination and Wellness-Wildlife-Water Tourist facility at Naya Raipur with a project cost of Rs. 200 crores.
- Funds for State Capital Region office, Setup and Survey including survey of Raipur-Durg Metro line.
- Funds for Indian Institute of Public Administration CG Chapter.
- Funds for Exposure Visits of Journalists and Budgetary provision for renovation of Office of Journalist Association. Patrakar Samman Nidhi amount to be doubled.
- Funds for Allotting land at subsidized rate for office of Chamber of Commerce at Nava Raipur.
- Social Audit of DMF works.
- Provision for Incentives based on Departmental Reforms (Competitive Index).
- Funds for Digitization of Land Records and Digital Crop Survey
Highlights
- New Medical College at Kunkuri District Jashpur
- Homestay Policy for promotion of Tourism in Bastar & Sarguja
- New Prayas Residential Schools at Balarampur & Rajnandgaon
- Funds for Bastar Olympics, Bastar Madai, Naya Raipur Bastar Marathon, Naya Raipur Golf Tournament etc.
Chhattisgarh’s Economy
- Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP): Chhattisgarh Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) at current prices is has increased from 5,12,107 Crore to 5,67,880 Crore, marking a growth on 11% in 2024-25 (RE). GSDP is expected to grow at 12% to reach ₹6,35,918 crore in 2025-26 against national growth of 10%.
- GSDP at constant price is expected to grow at 7.5%. This is higher than the National GDP is estimated to grow at 6.4% in 2024-25.
GDP Growth (FY 2024-25) (at constant price)
| GDP growth rate | Chhattisgarh | India |
| 7.5%. | 6.4% |
- Per Capita Income: In 2024-25, per capita income is expected to grow by to Rs 1,62,870 per annum which is lower than national per capita income of Rs 2,00,162 per annum which has grown by 8.66%.
Sectoral Contribution in GSDP (FY 2024-25) (at constant price)
| Factor | Chhattisgarh | India |
| Per Capita Income | Rs 1,62,870 | Rs 2,00,162 |
| Per Capita Income growth rate | 9.37% | 8.66%. |
- Sectors: In 2024-25, Agriculture sector is projected to grow by (as compared to national growth of), Industrial sector by 6.92% (as compared to national growth of and sector by (as compared to national growth of)
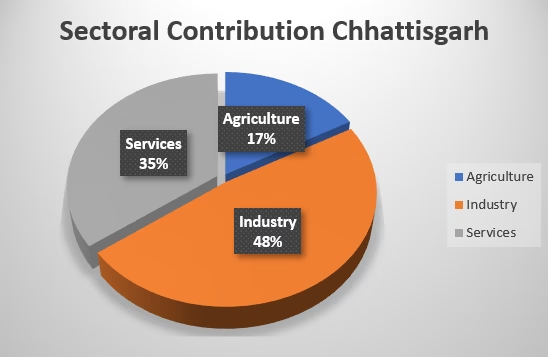
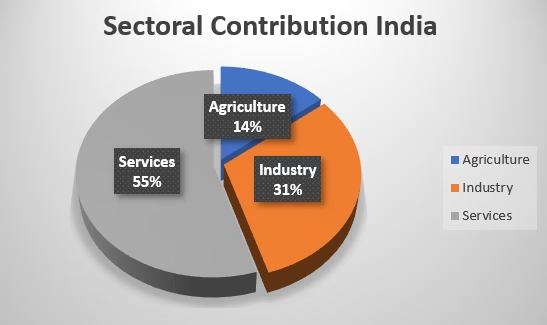
- In 2024-25 at constant price, the contribution in GSDP by Agriculture sector is 16.8% compared to 14.16% at national level, Industrial sector is 48% compared to 30.97% at national level and Service sector is 35% compared to 54.62% at national level. There is a focus of the Government to increase the contribution of service sector in the GSDP.
Sectoral Contribution in GSDP (FY 2024-25) (at constant price)
| Sector | Chhattisgarh | India |
| Agriculture | 16.8% | 14.16% |
| Industry | 48% | 30.97% |
| Services | 35% | 54.62% |
Sectoral Growth (FY 2024-25) (at constant price)
| Sector | Chhattisgarh | India |
| Agriculture | 5.36% | 3.76% |
| Industry | 6.92% | 6.22% |
| Services | 8.54% | 7.22% |
Receipts

Revenue Receipts (राजस्व प्राप्तियाँ):
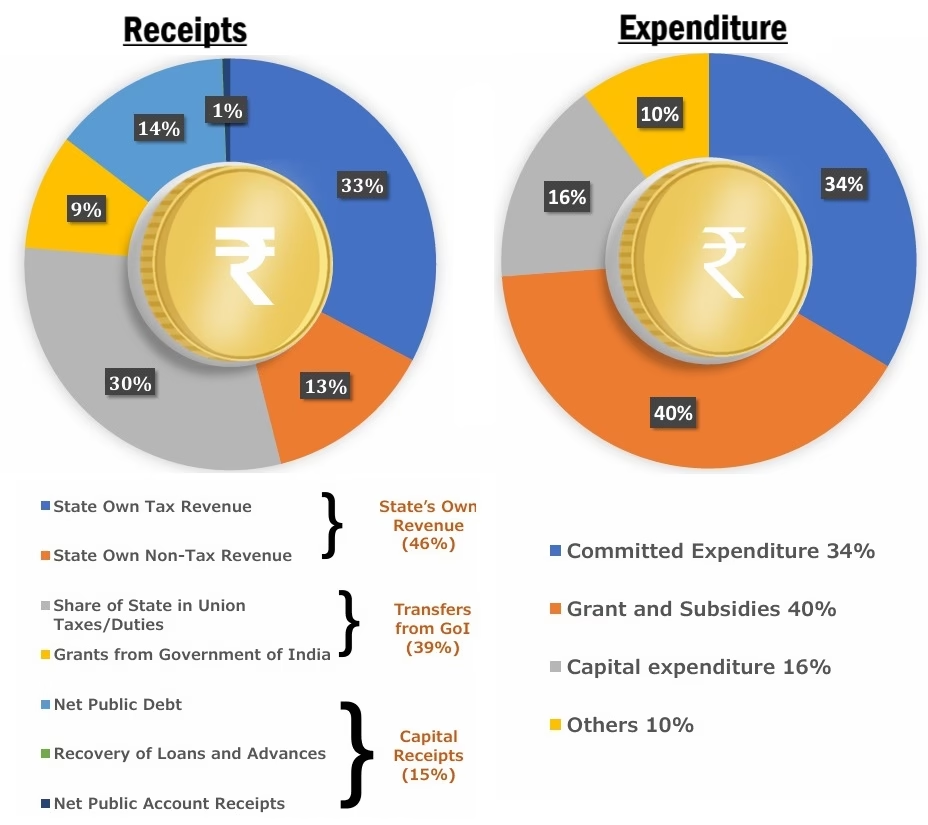
- The total revenue receipts for 2025-26 are estimated to be Rs 1,41,000 Crore (12% increase over 2024-25 (RE)). Of this Rs 76,000 Crore (54% of the revenue receipts) will be raised through State’s own resources and Rs 65,000 Crore (46% of the revenue receipts) from central transfers, i.e. State’s share in central taxes (35%) and grants-in-aid (11%) from the central government. It is 13% increase over central transfers received in 2024-25.
- State’s own revenue: Rs 76,000 Crore (54% of the revenue receipts) will be raised through State’s own resources (12% of GSDP). State’s own tax revenue is estimated to be Rs 54,000 Crore in 2025-26, an increase of 9% over that of 2024-25. State’s non-tax revenue is estimated to be Rs 22,000 Crore, an increase of 18% over that of 2024-25.
Capital Receipts (पूंजीगत प्राप्तियाँ):
- The main items of capital receipts public debt (लोक ऋण) is estimated to be Rs 23,000 Crore (22% lower than 2024-25 RE) which include market borrowings and from Banks, loans received from foreign governments.
- The total capital receipts for 2025-26 are estimated to be Rs 24,100 Crore which is 21.8% lower than 2024-25 (RE)
- The receipts from public account include small savings (Post-Office Savings Accounts, National Savings Certificates, etc), provident funds and net receipts obtained from the sale of shares in Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs). They are estimated to be Rs 1,000 Crore in 2025-26 (same as 2024-25 RE).
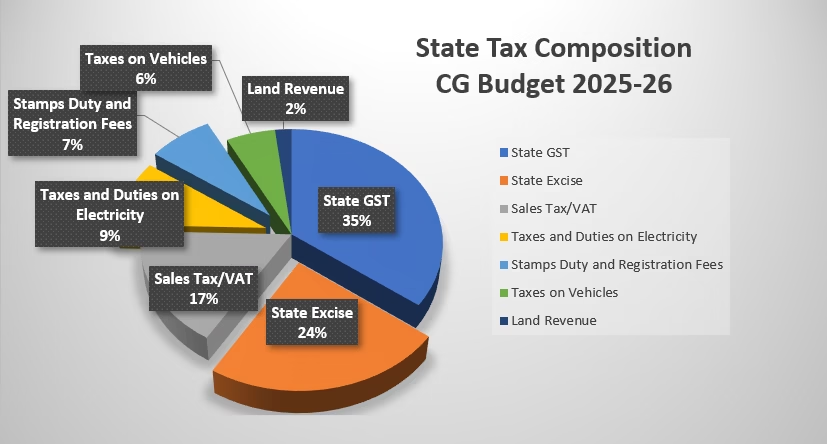
The major sources of State’s own tax revenue are:
| Head | 2024-25 (Revised-RE) | 2025-26 (Estimate-BE) |
| State GST | 17k Crore | 18.6k Crore 10.0% higher than 2024-25 (RE) |
| State Excise | 10.5k Crore | 12.5k Crore 19.0% higher than 2024-25 (RE) |
| Sales Tax/VAT | 6.5k Crore | 8.8k Crore 25.0% higher than 2024-25 (RE) |
| Taxes and Duties on Electricity | 4.5k Crore | 5.0k Crore 11.0% higher than 2024-25 (RE) |
| Stamps Duty and Registration Fees | 3.2k Crore | 4.0k Crore 25.0% higher than 2024-25 (RE) |
| Taxes on Vehicles | 2.5k Crore | 3.0k Crore 20.0% higher than 2024-25 (RE) |
| Land Revenue | 1.0k Crore | 1.0k Crore |
Expenditure
Capital Expenditure (पूंजीगत व्यय):
- Capital expenditure for 2025-26 is proposed to be Rs 26,341 Crore (18.0% increase over 2024-25 RE) which include expenditure affecting the assets and liabilities of the state, such as: (i) capital outlay, i.e. expenditure which leads to creation of assets (such as bridges and hospitals), and (ii) repayment and grant of loans by the state government.
- Debt Servicing (Debt Repayment) for 2025-26 constitutes about Rs 11,337 Crore (6.8% of Total Expenditure).
Revenue Expenditure (राजस्व व्यय):
- Revenue expenditure includes payment of salaries, pension, subsidies, grant and interest etc.
- Revenue expenditure for 2025-26 is proposed to be Rs 1,38,196 Crore (11.0% increase over 2024-25 RE)
- Debt Servicing (Interest Payments) for 2025-26 constitutes about Rs 9,515 Crore towards making interest payments (ब्याज भुगतान).
- Committed expenditure: Committed expenditure of a state typically includes expenditure on payment of salaries, pensions, and interest. In 2025-26, Chhattisgarh is estimated to spend Rs 55,231 Crore on committed expenditure, which is 39% of estimated revenue receipts.
| Committed Expenditure | 2024-25 (Revised-RE) | 2025-26 (Estimate-BE) |
| Salary | 30.8k Crore | 35.3k Crore (25% of revenue receipts) |
| Pension | 9.5k Crore | 10.3k Crore (7% of revenue receipts) |
| Interest Payments | 9.0k Crore | 9.5k Crore (6.7% of revenue receipts) |
Loans and Advances (ऋण एवं अग्रिम):
- Loans and Advancers for 2025-26 is estimated to be Rs 463 Crore which is 54.3% higher than 2024-25 (RE).cg budget 2025-26 expenditures
Receipts Vs Expenditure
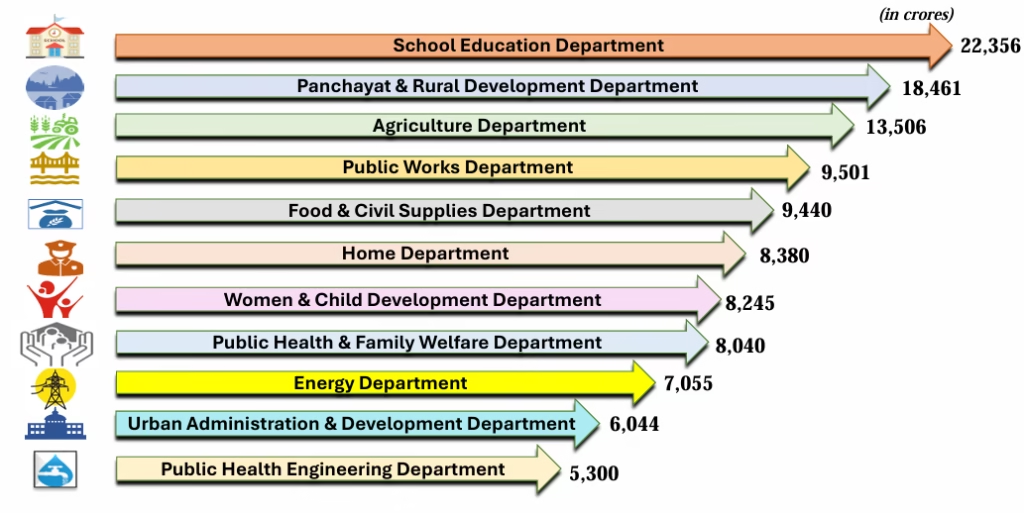
Sector-wise Budget Allocation
15th Finance Commission’s Recommendations for 2021-26
The 15th Finance Commission’s (FC) report for the 2021-26 period was released on February 1, 2021. For the 2021-26 period, the Commission has recommended the share of states in the divisible pool of central taxes to be 41%. This is 1% point lower than the 42% share recommended by the 14th FC (for the 2015-20 period) to separately provide funds for the newly formed union territories of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh.
The 15th FC proposed revised criteria for determining the share of individual states (different from 14th FC). The Commission has prescribed certain conditions like transparency in accounts and improvement in property tax collections for availing these grants.
Based on the 15th FC’s recommendations for the period 2021-26, Chhattisgarh will have a 1.40% share in the divisible pool of central taxes. This implies that out of every Rs 100 of revenue in the divisible pool during the 2021-26 period, Chhattisgarh will receive Rs 1.40. This is higher than Rs 1.29 recommended by the 14th FC.
The 15th Finance Commission recommended the following fiscal deficit targets for states for the 2021-26 period (as a % of GSDP):
(i) 4% for 2021-22, (ii) 3.5% for 2022-23, and (iii) 3% for 2023-26.
As per the 15th FC recommendations, Chhattisgarh is expected to receive Rs 10,368 Crore as local body grants between 2021-2026. As of 2022-23, it has received Rs 4,791 Crore as local body grants. For 2024-25 (RE) and 2025-26, it is estimated to cumulatively receive Rs 3,511 Crore.
Public Debt Composition
Constitutional Provisions:
- Article 292: Government of India can borrow amounts specified by the Parliament from time to time.
- Article 293: State Governments in India can borrow only from internal sources.
Thus, the Government of India incurs both external and internal debt, while State Governments incur only internal debt.
Public Debt: Debt contracted against the guarantee of Consolidated Fund of India or State (defined as Public Debt)
- Internal debt: owed to lenders within the country.
- The government borrows by issuing the Government Bonds and T-Bills (Treasury Bills).
- Securities issued to International Financial Institutions
- Borrowing from RBI under Market Stabilization Scheme (MSS) Bonds for sterilization operations
- External debt: owed to creditors outside the country
- The outsider creditors can be foreign governments, International Financial
Institutions such as World Bank, Asian Development Bank etc., corporate and
foreign private households. - External debt may be of several kinds such as multilateral, bilateral, IMF loans, Trade
credits, External commercial borrowings etc. - When the non-resident Indians park their funds in India, it is also a type of external debt and
is called NRI deposits.
- The outsider creditors can be foreign governments, International Financial
Public Debt (Chhattisgarh)
| Details | 2024-25 (RE) | 2025-26 (BE) |
| Receipts | 39.0k Crore | 34.3k Crore |
| Repayment | 9.3k Crore | 11.3k Crore |
| Net Public Debt | 29.6k Crore | 23.0k Crore |
Other Liabilities: Liabilities in the Public Account (called as Other Liabilities)
- Liabilities on account of Provident Funds
- Reserve Funds and Deposits, Other Accounts, etc
- Securities issued against ‘Small Savings’: All deposits under small savings schemes are credited to the National Small Savings Fund (NSSF). The balance in the NSSF (net of withdrawals) is invested in special Government securities.
Public Account (Chhattisgarh)
| Details | 2024-25 (RE) | 2025-26 (BE) |
| Receipts | 2.41 Lakh Crore | 2.49 Lakh Crore |
| Repayment | 2.40 Lakh Crore | 2.48 Lakh Crore |
| Net Other Liabilities | 1.0k Crore | 1.0k Crore |
Outstanding Liabilities:
Outstanding liabilities is the accumulation of total borrowings at the end of a financial year, it also includes any liabilities on Public Account. At the end of 2023-24, the outstanding liabilities are
Outstanding Liabilities (Chhattisgarh)
| Details | 2022-23 | 2023-24 | 2024-25 (RE) |
| Outstanding liabilities | 1.01 Lakh Crore | 1.34 Lakh Crore | 1.64 Lakh Crore |

Economy of India and Chhattisgarh

 Home
Home Syllabus
Syllabus Contact Us
Contact Us




