Definitions of Disaster:
- Hazard: Possible dangerous situation, occurs due to natural or manmade activity, have the potential to affect life and property
- Vulnerability: Extent to which life and property can get affected
- Capacity: Ability to cope or decrease the vulnerability
- Disaster: A hazard with high vulnerability beyond the coping capacity which are catastrophic in nature
- 27 of 35 States are disaster prone
Disasters cannot be totally prevented. However early warning systems, careful planning and preparedness on part of the vulnerable community would help in minimizing the loss of life and property due to these disasters.
Types: a generic categorization of disasters could be made that would include:
- Water and Climate related, such as floods, droughts, cyclones, tsunami
- Geologically related, such as earthquakes, landslides, sea erosion, dam bursts
- Chemical, Industrial and Nuclear related
- Accident related
- Epidemics
Factors aggravating Disaster:
- Physical:
- Land use, urbanization
- Heavy structures like dams, roads
- Social:
- Literacy, social practices
- Population growth
- Economic:
- Poverty,
- Industries, mining
- Environmental:
- Loss of biodiversity, natural resources depletion
- Technological:
- Lack of awareness
- Lack of advance warning systems
- Lack of mitigation techniques
Key Disasters in India: Earthquake, Flood, Cyclone, Landslide, Tsunami, Droughts
Disaster Management:
There is a paradigm shift worldwide from a traditional relief approach to disaster preparedness.
- A more holistic and long-term strategy which incorporates vulnerability reduction as part of the development planning process.
- This comprehensive approach recognizes the fact that disaster reduction is most effective at the community level if the specific local needs are met.
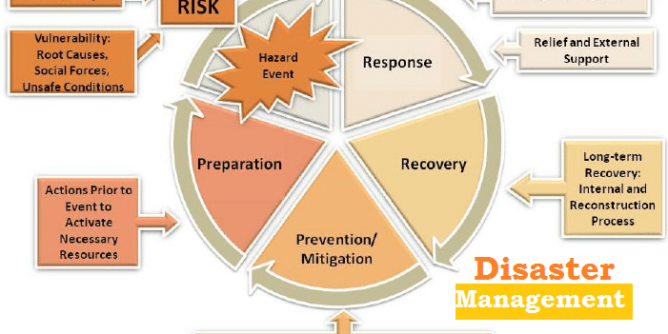
Components of Disaster Management
Pre- disaster phase: (CPP)
- Capacity Building:
- Human resource development
- Organizational development
- Institutional and legal framework development
- Prevention and Mitigation:
- Risk Assessment and Vulnerability Mapping
- Environmentally Sustainable Development
- Climate Change Adaptation
- Preparedness:
- Role of administration including community participation
- Forecasting and Early Warning Systems
- ICT Support
- Medical Preparedness and Mass Casualty Management
- Training, Simulation and Mock Drills
Post-disaster phase: (RRR)
- Response:
- Role of State, District and Local Authorities
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
- Medical Response
- Rehabilitation:
- Setting up of Temporary Relief Camps
- Reconstruction and recovery
Challenges: Disaster management is in the State List with Public Health (2nd ARC Report has recommended including it in the Concurrent List) is the main challenge among others which obstructs uniformity in tackling disasters.
The Disaster Management Act, 2005
- Institutional mechanism:
- National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) under the Chairmanship of the PM
- State Disaster Management Authorities (SDMAs) under the Chairmanship of the CMs
- District Disaster Management Authorities (DDMAs) under the Chairmanship of Collectors/District Magistrates/Deputy Commissioners
- Specific roles for local bodies
- National Executive Committee (NEC) acts as administrative body consisting of Secretaries of relevant ministries headed by Cabinet Secretary
- Financial mechanism:
- National Disaster Mitigation Fund and National Disaster Response Fund
- Funds at the state and district levels
- Capacity building:
- National Institute of Disaster Management (NIDM)
- Disaster response:
- National Disaster Response Force (NDRF) with the help of Central Para Military Forces
- Similar forces at State and District level
- Civil Defence Force (comprising PRI and NGOs)
- Problems:
- No regular and very few meetings of all institutions
- No disaster expert in the institutions
- NDMA is not empowered to take action against the States for non-compliance
- Disaster Mitigation Funds yet to be constituted (in some States)
- Non-existence of Disaster Response Forces at State and District level
- Non-participation of local institutions in the form of Civil Defence Force
- Warning and forecasting agencies work in isolation

 Home
Home Syllabus
Syllabus Contact Us
Contact Us