Category: PSC Pre
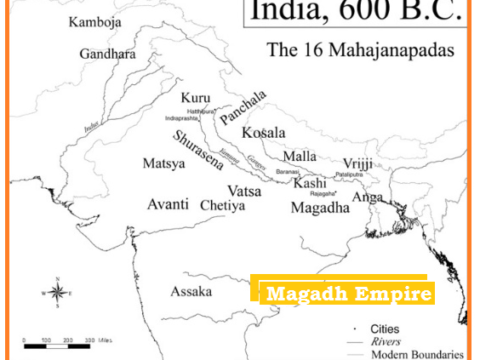
Rise of Magadh Empire
From the 6 century BC, the material advantages paved the way for the establishment of territorial kingdoms after Vedic period. ‘Jana’ or tribe was now given lesser importance as people…
Vedic Civilization
Vedic Civilization started with the arrival of Aryans into the Indian Sub-continent and settled in the Indus region (known as land of seven rivers ‘Saptasindhu’) around 1500 BC from Central…
(Practice Quiz) CG PSC 2012 Pre (Paper 1)
Attempt this in time-limit to have a feel of real examination.
Contribution of Indian Mathematicians
Aryabhata (5th– 6th century AD, Patliputra) 2015 (20’) 2012 (40’) Aryabhata is the author of several treatises on mathematics and astronomy. Some of the important works are Aryabhatiya and Arya-siddhanta. Major Contribution to…
Schedules of the Constitution
Schedules are lists in the Constitution of India that categorize activities and policy of the Government. Indian Constitution had originally eight schedules, which with further additions became twelve as of…
Amendment of the Constitution
Art 368 deals with the powers of the Parliament to amend the Constitution and its procedure. The amendment procedure laid down is rigid and flexible; flexible to include the changed…
Emergency Provisions in the Constitution
Art 352- Art 360 deal with emergency provisions, incorporated to safeguard the sovereignty, unity and integrity of the country. These provisions empower the Union Govt to meet certain unforeseen emergencies…
Official Language- Language of the Union and Regional Languages
Part XVII (Art 343- 351) deals with Language of the Union and Regional Languages. Provisions are divided into four heads: 1. Language of Union: Hindi written in Devanagari script is to…
Panchayats and Municipalities
The history of Panchayati Raj starts from the self-sufficient and self-governing village communities. In the time of the Rig-Veda (1700 BC), evidence suggests that self-governing village bodies called ‘sabhas’ existed. With the…
Special Provisions Relating to Certain Classes
Constitution provides for safeguarding the interests of certain classes for equality and justice (as enshrined in the Preamble).Part XVI (Art 330- 342) details the special provisions relating to SC/ST/OBCs and…

 Home
Home Syllabus
Syllabus Contact Us
Contact Us