
Satellite Programmes
1. Aryabhata: India’s first satellite was launched by the Soviet Union on 19 April 1975.
2. The INSAT series:
- INSAT (Indian National Satellite System) is a series of multipurpose geostationary satellites
- For telecommunications, broadcasting, meteorology and search-and-rescue needs of India.
3. The IRS Series:
- Indian Remote Sensing satellites (IRS) are a series of earth observation satellites
- It provides remote sensing services to the country.
- All the satellites are placed in polar Sun-synchronous orbit
- The initial versions are composed of the 1 (A, B, C, D) nomenclature. The later versions are named based on their area of application including OceanSat, CartoSat, ResourceSat
4. Radar Imaging Satellite (RISAT):
- ISRO currently operates two Radar Imaging Satellites. RISAT-1 was launched from Sriharikota Spaceport on 26 April 2012
- RISAT-1 carries a C-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) payload to provide images with high resolutions.
5. GSAT Series:
- GSAT series of geosynchronous satellites is a system developed by ISRO with an objective to make India self-reliant in broadcasting services.
- Extended C and Ku-bands provides services to telecommunications, television broadcasting, weather forecasting, disaster warning and search and rescue operations.
GSLV Mission
- Launched due to increasing communication needs
- Can carry more than 2 tonnes load
- Placed at 36000 km in Geostationary Transfer Orbit (GTO)
- It is bigger, lighter and more efficient than PSLV
- Uses cryogenic engine for upper stages
Indigenous GSLV Mission:
- India was using Russian cryogenic engine for GSLV mission
- Indigenous development was under progress
- 2010 GSAT satellite launch failed which was using Russian engine
- 2013 with Indian engine was aborted when a leak was detected in the fuel system
- 2014 mission accomplished
GSLV Mark III:
- To use cryogenic engine (-150 0C) with liquid O2 and liquid H2 propellant
- Largest launch vehicle program till now by ISRO
- Forerunner to manned mission to space
Astrosat:
- First dedicated multi-wavelength space observatory (Similar to NASA’s Hubble Telescope)
- In a select club of USA, EU, Japan, Russia
- To understand neutron stars and black holes
Solar Mission: Aditya-I
- India’s first solar mission slated for lift off in 2018-19
- Data collected will be useful for studying the origin of the solar storms
- The point where the spacecraft will be positioned is called Lagrangian-1
Reusable Launch Vehicle
ISRO successfully flight tested India’s first Reusable Launch Vehicle-Technology Demonstrator (RLV-TD) vehicle operating in hypersonic flight regime.
Major Parts:
- Aero-thermodynamic characterization of the vehicle with wings when it re-enters the atmosphere at hypersonic speed;
- The control and guidance system;
- The control system to land the vehicle at a specific location;
- The hot structure, the basic body-carrying part of the vehicle with heat protecting tiles.
Advantages:
- It would be cutting down by as much as 80% the cost of launching satellites into orbit. The bulk of the launch cost comes from building the rocket, which can be used just once, as the rockets get burnt on re-entry into the atmosphere.
- No other space agency has reusable launch vehicles in operation, and ISRO has taken a lead in developing one.
- Though it will take 10 to 15 years, and several more launches, before ISRO readies a reusable launch vehicle for commercial use.
Scramjet Rocket Engine
ISRO successfully launched a rocket using a scramjet engine that was developed indigenously
Features:
- A scramjet engine uses oxygen present in the atmospheric air to burn the hydrogen fuel.
- As a result, the amount of oxygen required to be carried on board would be reduced considerably as atmospheric oxygen is utilized to burn the fuel in the first stage.
- However, it works for higher speeds (>Mach 5) only (a Ramjet engine requires for lower speeds)
- A ramjet engine also uses atmospheric air for the combustion but it slows down the pressurized air velocity before letting in to the combustor
Significance:
- Therefore, rockets fired by scramjet engines will be able to carry more payloads.
- They are more efficient
- Forerunner to manned mission to space
Navigation with Indian Constellation (NAVIC)
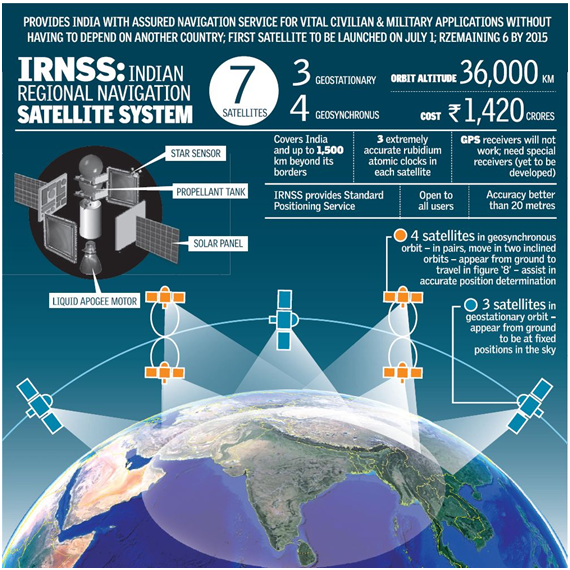
- India’s indigenous navigation system with a constellation of 3 Geostationary and 4 Geosynchronous satellites
- Geostationary: Satellites remain at a particular distance from earth at all the time, so in circular orbits (in the plane of equator on the earth)
2014 (02) - Geosynchronous: It has a period of revolution is equal to period of rotation of earth, but its orbit is neither equatorial nor Circular and looks oscillating but NOT stationary.
- The system will be similar to the GPS (United States), Glonass (Russia), Galileo (Europe)and BeiDou (China)
- An area of 1,500 km from Indian boundaries will be covered under the navigational system.
- It has two types of services- Standard Positioning System (SPS) for all users and Restricted Service (RS) for only authorised users like defence services.
Applications of IRNSS:
- Terrestrial, Aerial and Marine Navigation
- Traffic management and control
- Disaster Management
- Resource mapping
- GPS based logistic management (courier, PDS supplies)

 Home
Home Syllabus
Syllabus Contact Us
Contact Us





1 thought on “Space Program in India”