
The United Nations is an international organization founded in 1945 after the World War II. Its charter was signed in San Francisco on June 26, 1945 and came into existence on October 24, 1945 after 51 countries have signed the charter. The name “United Nations”, coined by United States President Franklin D. Roosevelt was first used in the Declaration by United Nations of 1 January 1942, during Second World War.
Background:
Its predecessor, the League of Nations, created by the Treaty of Versailles in 1919 was disbanded in 1946.
In 24 October 1945, at the end of World War II, the organization was established with the aim of preventing future wars. At its founding, the UN had 51 member states; there are now 193.
Mission:
- Maintaining international peace and security
- Developing friendly relations among nations
- Promoting social progress, better living standards and human rights
- Be a centre for harmonizing the actions of nations
| Headquarter: | New York |
| Official Languages: | Arabic, English, French, Chinese, Spanish, Russian |
| Members: | 193 (Latest Member South Sudan) |
| Secretary General: | Antonio Guterres (Portugal) |
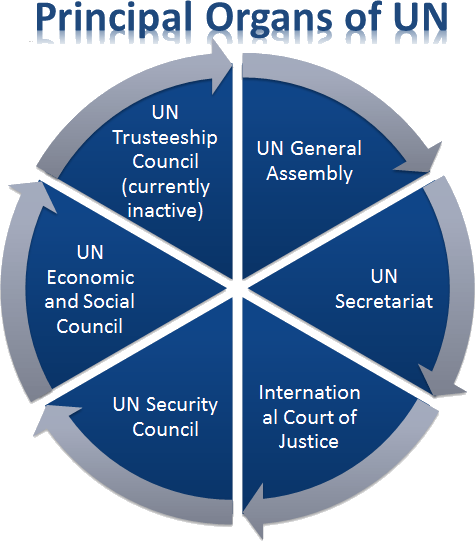
The UN has six principal organs:
- General Assembly;
- UN Secretariat;
- International Court of Justice
- Security Council;
- Economic and Social Council;
- Trusteeship Council;
General Assembly (UNGA)
It is the Main Deliberative Organ of United Nations.
Members: All member states, each of which has one vote.
Appointment:
- General Assembly appoints Secretary General of UN based on the recommendations given by Security Council.
- Elects Non-Permanent members in Security Council and elects Members for Social and Economic Council and elects Judges to International Court of Justice.
Decision and Recommendation:
- Decision on important questions such as those on peace and security, UN budget, admission, suspension and expulsion of members to various organs of UN requires special majority.
- All other questions are decided by a majority vote.
- The resolutions are not binding on the members.
- Make recommendations on any matters within the scope of the UN, except matters of peace and security that are under consideration by the Security Council.
UN budget:
- By its member states through compulsory and voluntary contributions.
- The size of each state’s compulsory contribution depends mainly on its economic strength, though its state of development and debt situation are also taken into account.

 Home
Home Syllabus
Syllabus Contact Us
Contact Us




