Good Governance
Good Governance is defined as the manner in which power is exercised in the management of a country’s economic and social resources for development.
As per World Bank, its various dimensions are:
- Public sector management
- Accountability
- Legal framework for development
- Transparency and accessibility
Characteristics of Good Governance:

- Civic Participation: of citizens in decision making process
- Transparency: accessibility to information
- Accountability: towards citizens
- Rule of law: checking arbitrary use of authority
- Responsiveness: to the needs
- Equity and inclusiveness: citizens not excluded from participation
- Consensus oriented: decision based on consensus
- Effectiveness and efficiency: result oriented
Governance from New Public Management (NPM):
- Governance assumed significance in late 1980s with the advocacy by World Bank
- World Bank has reinvented it as a new approach to development.
- Globalization has resulted in global pressures exerted by institutions in the form of economic reforms.
NPM Vs Governance:
- NPM focuses on processes with a view to achieving efficiency and performance. Governance emphasizes on interaction amongst Govt, market and civil society in realizing desired outcomes.
- NPM considers citizens as consumers of services who get benefit from efficiency. Governance assigns a significant position to citizens in decision making.
Government to Governance:
- Government (traditional approach) was based on the premise that Govt was solely responsible for formulating and implementing policy decisions.
- There has been excessive reliance on bureaucratic forms of organization, hierarchy, adherence to rules and regulations.
Governance to Good Governance:
- Failure of economic reforms in some African countries and collapse of centrally planned economies raised critical questions about governance system.
- The World Bank in a report considered the major factor was the failure of public institutions.
- As a result, the need for Good Governance was emphasized.
- Governance widened the scope of Public Administration beyond formal Govt. it extends up to the private sector, non-Govt mechanisms, collective decision making.
- The changing nature of the concept of development transformed the Governance. Development is determined by progress in all spheres- political, social, environmental with economic.
- Development is a process of creating suitable enabling environment for people to lead long, healthy, productive and creative lives.
Therefore, Governance processes need to be effective and efficient, this led to Good Governance.
Good Governance in India:
- Evolving a citizen-centric bureaucracy
- Right to Information, transparency
- Public grievance machinery
- Code of ethics
- Citizen charter
- Panchayati Raj Institutions (Decentralization)
Critique of Good Governance:
Good Governance attempts to ingrate political elements, economic aspects and social processes to foster holistic development. However, it seems to ‘depoliticize’ Govt and bring in more technical aspects at the cost of citizen’s democratic right to govern.
E-Governance
Electronic governance or e-governance is the application of information and communication technology (ICT) for delivering government services, exchange of information, communication transactions, integration of various services.
While Good Governance relates to safeguarding the democratic rights and providing equal opportunities to all citizens, ensuring equitable access to public services and being transparent in its dealing improves the quality of Good Governance.
Types of Government Interactions:
- G2G (Government to Government): enables seamless interaction between various government entities
- G2C (Government to Citizen): interaction between the government and the citizens
- G2B (Government to Business): enables the business community to interact with the government by using e-governance tools
- G2E (Government to Employee): interaction between the government and its employees
National e-Governance Plan:
- It is an initiative of the Government of India to make all government services available to the citizens of India via electronic media.
- The Government approved the National e-Governance Plan, consisting of 27 “Mission Mode Projects” (MMPs) and Ten components, on 18 May 2006.
- This is an enabler of Digital India initiative, and UMANG (Unified Mobile Application for New-age Governance) in turn is an enabler of NeGP.
E-Governance Initiatives in Govt of India:

Digital India Initiative: It is an umbrella program to prepare India for a knowledge-based transformation.
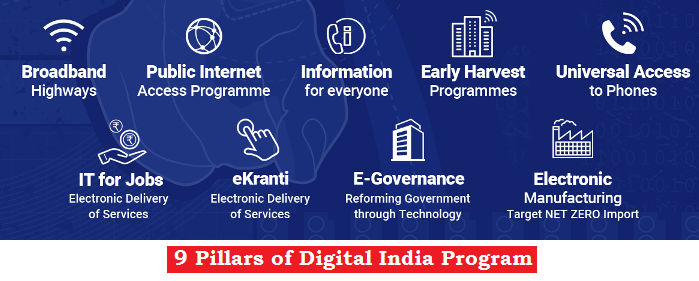
- MyGov: It aims to establish a link between Government and Citizens towards meeting the goal of good governance. It encourages citizens as well as people abroad to participate in various activities i.e. ‘Do’, ‘Discuss’, ‘Poll’, ‘Talk’, ‘Blog’, etc.
- DigiLocker: It serves as a platform to enable citizens to securely store and share their documents with service providers who can directly access them electronically.
- National Scholarships Portal (NSP): It provides a centralized platform for application and disbursement of scholarship to students under any scholarship scheme.
- PRAGATI (Pro-Active Governance And Timely Implementation): It is also a robust system for bringing e-transparency and e-accountability with real-time presence and exchange among the key stakeholders.
- Common Services Centres 2.0 (CSC 2.0): It is being implemented to develop and provide support to the use of information technology in rural areas of the country.
- Jeevan Pramaan: It is an Aadhaar based Biometric Authentication System for Pensioners.
- National e-Governance Plan (NeGP): It comprises of 31 Mission Mode Projects, approved in 2006, but later it was integrated into Digital India Program.

UMANG (The Unified Mobile Application for New-age Governance) is a Government of India all-in-one single unified secure multi-channel multi-platform multi-lingual multi-service freeware mobile app for accessing over 623 services.
Recent Services Based on e-Governance:
- Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT): to facilitate disbursements of Government entitlements like MNREGA, Social Security Pension, LPG subsidy, etc. using Aadhar.
- Aadhar Enabled Payment System (AEPS): financial services- withdrawal, deposit, transfer, etc using Aadhar authentication
- BHIM App: Bharat Interface for Money (BHIM) is an app that lets one make simple, easy and quick payment transactions using Unified Payments Interface (UPI).
E-Governance Initiatives by Chhattisgarh Govt:
- CG Bhuiyan: computerization of land records and availability of land maps online
- CM Jandarshan: online portal for receiving citizens’ grievances
- Common Service Centers (CSCs): many Govt services like caste, income, birth/death certificates, and financial services, etc are provided by these centers.
- e- Challan: for making government payments viz. sales tax, excise duty, professional tax, land revenue etc.
- CG Haat: online platform for buying and selling vegetables, fruits etc (launched during Covid-19 Lockdown)
- CG Awas: single window clearing system for getting all kind of approvals for establishing residential colony within 100 days.
Advantages of e-Governance:
- Enhanced speed: technology increases the speed for communication
- Reduced cost: cost of stationary, printers, no physical movement required, etc is greatly reduced.
- Transparency in activities of Govt: information related to Govt and various services are made available on the internet which increases the transparency of the activities.
- Accountability for Govt machinery: transparency and accountability go hand-in-hand. Information available to be accessed by the public can be used to make the Govt accountable.
- Convenience for citizens: E-Government brings public services to citizens on their flexibility of time and place.
- Improved Customer Service: E-Government allows re-deployment of resources from back-end processing to the front line of customer service.
Disadvantages of e-governance:
- No personal interaction: no person is available to clarify doubts based on the information available online, which might be less useful for laymen.
- High technology requirement: the implementation of an e-government service requires high technology requirement like server maintenance, high internet speed, website security, etc.
- Digital illiteracy: e-governance services are not useful for some section of the society- rural populace, less educated people, senior citizens, etc as they are not accustomed with the digital world.
- Security and privacy breach: even with high web security, the public are still concerned over security, fear of spam, fishing, hacking, etc. The misuse of personal data and online monitoring of activities still holding back the citizens to avail the e-services fully.

 Home
Home Syllabus
Syllabus Contact Us
Contact Us