BCIM Forum
The BCIM (Bangladesh–China–India–Myanmar)Forum for Regional Economic Cooperation, earlier known as the ‘Kunming Initiative’, was founded in 1999 with the objective of promoting trade and economic development in the sub-region stretching from south west China to eastern India (‘Kunming to Kolkata’) via Myanmar, India’s north east region (NER), and Bangladesh.
| Table of Contents: |
| BCIM Forum: Areas of Cooperation BCIM Economic Corridor Indian Concerns in BCIM Corridor Importance of BCIM Mekong Ganga Cooperation (MGC): Areas of Cooperation Structure |
Areas of Cooperation
- Physical Connectivity
- Trade in goods, services and investment including finance
- Environmentally sustainable development
- People to people contacts
BCIM Economic Corridor
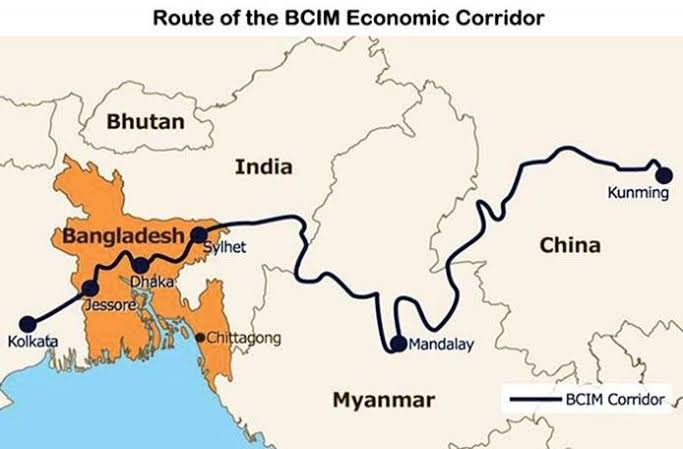
- It is a multi-modal corridor will be the first expressway between India and China and will pass through Myanmar and Bangladesh.
- It’s a Cross- border transport facility passing through Kolkata, Silchar (Assam) and Imphal in India.
- It would connect Kolkata to Kunming via Dhaka (Bangladesh) and Mandalay (Myanmar).
Indian Concerns in BCIM Corridor
- Insurgency in North East India and Myanmar:
- There are still several insurgent and rebel groups in North East India which are involved in a host of anti national activities like gun running, drug trafficking; they are also being used by foreign intelligence agencies.
- There have also been reports of some Chinese intelligence agents being active there; ISI has also been involved in sending arms.
- Sino-Indian border problems:
- Indian sensitivities concerning the claims and possible insecurities on that account.
- Even though some funds for constructing Ledo/Stilwell Road have been earmarked, India is not in favour of reviving the old Burma/Stillwell Road linking India’s NE to Yunnan through Myanmar because of security reasons.
- There are apprehensions that this might give China advantage in case of a military conflict.
- Growing trade imbalance:
- There is a growing trade imbalance between India and China and any free flow of trade and commerce through the envisioned economic corridor would only increase the trade imbalance against India as China..
- Several multilateral initiatives:
- India has several bilateral and multilateral initiatives with the regional countries to address precisely the same issues.
- For instance, India has Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC), Mekong Ganga Cooperation initiative and Trilateral between India, Myanmar and Thailand for improving connectivity.
- All such initiatives involve either cooperation with Bangladesh or Myanmar or both that have similar objectives to that of BICM.
Importance of BCIM
- Development of North East India:
- BCIM helps India in developing infrastructure in NE areas which further helps India in engaging with Myanmar and Bangladesh.
- India will benefit in terms of the development of the Kolkata port and the opening up of the economic potential of the northeast states.
- India’s Act East Policy:
- BCIM can not only be a game-changer for this region in Asia, but is also pivotal for India’s ‘Act East’ Policy.
- India’s gain from the BCIM includes the ability to connect to the One Belt, One Road project thus opening up markets to the east.
- Foreign relationship:
- BCIM offers India an opportunity to create its own win-win relationship with China. It provides China with access to Bay of Bengal bypassing the Straits of Malacca.
- Regional connectivity and trade:
- Economic Benefits include access to several booming markets in Southeast Asia, improvement of transport infrastructure and setting up of industrial zones.
- The regional connectivity would facilitate cross-border movement of people and goods, reduce overland trade bottlenecks, ensure access and increase volume of trade.
- Substantially reduce transaction costs, enhance trade and investment and poverty alleviation in the region.
- With natural gas reserves of about 200 trillion cubic feet, the largest in the Asia-Pacific, Bangladesh could become one of the major energy exporting countries.
- Cultural integration:
- BCIM will help in cultural integration between all member countries because of their cultural unanimity.
- Tourism boost:
- Tourism too will get a boost in the region.
Mekong Ganga Cooperation (MGC)
The Mekong Ganga Cooperation (MGC) was established on November 10, 2000, at Vientiane, Laos at the First MGC Ministerial Meeting. It comprises six member countries, namely India and five ASEAN countries of Mekong basin– Thailand, Myanmar, Cambodia, Laos and Vietnam. (China is not included)
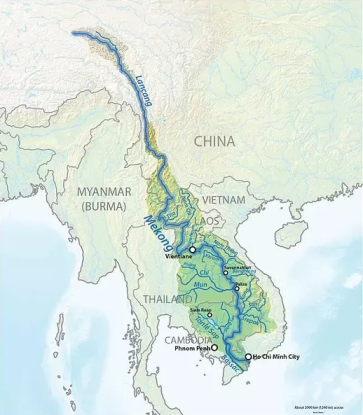

The organization takes its name from the Ganga and the Mekong, two large rivers in the region. Both the Ganga and the Mekong are civilizational rivers, and the MGC initiative aims to facilitate closer contacts among the people inhabiting these two major river basins. The MGC is also indicative of the cultural and commercial linkages among the member countries of the MGC down the centuries.
Areas of Cooperation
The four areas of cooperation are tourism, culture, education, and transportation.
Structure
The working mechanism for MGC consists of the Annual Ministerial Meeting (back to back with ASEAN Ministerial Meeting), the Senior Official’s Meeting, and Working Groups.
The ninth Mekong-Ganga Cooperation Meeting was held in Singapore on August 2, 2018.
The most visible manifestation of MGC is the MGC Museum of Traditional Asian Textiles at Siem Reap, Cambodia, established with Indian assistance in April 2014.

 Home
Home Syllabus
Syllabus Contact Us
Contact Us