For Basics of State Finance and Budget, please go through Fiscal Policy: Budget, Fiscal Deficit, Public Debt.
This is the first budget presented by newly formed government as “Amritkaal ke neev ka Budget”. The
budget is focused on the prosperity for Gareeb, Yuva, Anndata & Naari (GYAN) and stimulating infrastructural growth by increasing capital expenditure, and employment & livelihood promotion for youth of the state. The budget is an important step towards fulfilling promises under “Modi ki Guarantee”.
Amritkaal: Chhattisgarh Vision @2047:
As stated by the finance minister 10 Fundamental Strategical Pillars which will assist to achieve the mid-term target to double our state’s GSDP in next 5 years from 5 lakh crores to 10 lakh crores by year 2028 and long-term goals by 2047 with a vision to emerge as a developed state in the Amritkaal.
- Focus of our Economic Development: Gareeb, Yuva, Anndata&Naari (GYAN)
- Rapid Economic Growth through Technology driven Reforms in Governance
- Maximum capital expenditure
- Optimum utilization of Natural Resources
- Emphasis on new possibilities of service sector of the economy
- Ensuring private investment
- Focus on Bastar-Surguja
- Decentralized Development Pockets (DDP)
- Promoting Chhattisgarhi Culture
- Importance of Implementation
Chhattisgarh’s Economy
- Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP): Chhattisgarh Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) at constant price is expected to grow at 6.5%, compared to 8% in 2022-23. This is lower than the National GDP is estimated to grow at 7.3% in 2023-24.
- At current prices, the Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) is projected to increase from Rs 4,64,399 Crores in 2022-23 to Rs 5,05,886 Crores in 2023-24, which is an increment of 8.93%.
- Per Capita Income: In 2023-24, per capita income is expected to grow by 7.31% to Rs 1,47,361 per annum which is lower than national per capita income of Rs 1,85,854 per annum which has grown by 7.9%.
- Sectors:
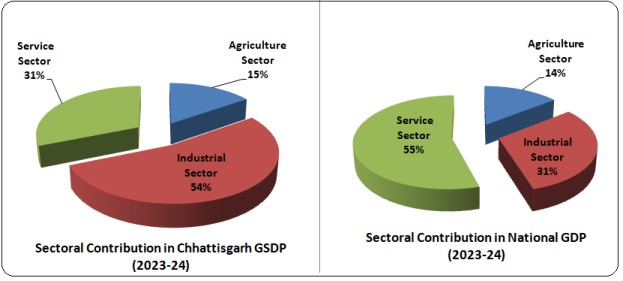
- In 2023-24, Agriculture sector is projected to grow by 3.23% (as compared to national growth of 1.82%), Industrial sector by 7.13% (as compared to national growth of 7.93% and Services sector by 5.02% (as compared to national growth of 7.72%) at constant price.
- In 2023-24, the contribution in GSDP by Agriculture sector is 15.32% compared to 14.41% at national level, Industrial sector is 53.50% compared to 30.97% at national level and Service sector is 31.19% compared to 54.62% at national level. There is a focus of the Government to increase the contribution of service sector in the GSDP.
Chhattisgarh Budget Analysis (2024-25)
Budget Highlights
- The Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) is estimated to be Rs 5,61,736 Crore which is 11.0% higher than 2023-24 (RE).
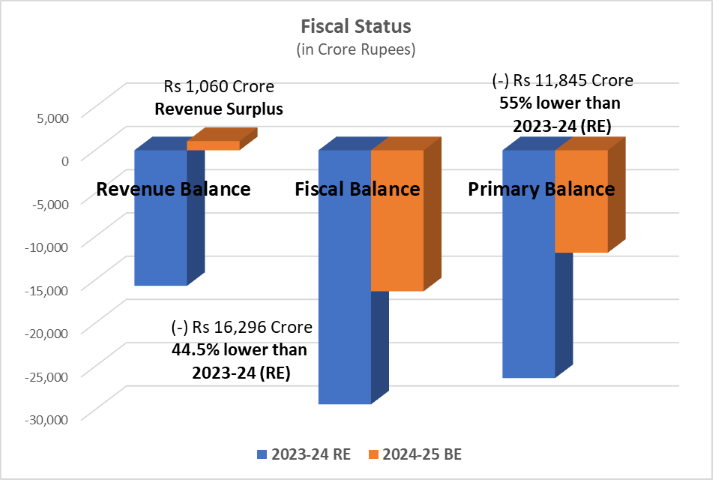
- The Fiscal Deficit is estimated to be Rs 16,296 Crore which is 2.90% of GSDP. This is within the limit of 3% set in the FRBM Act.
- Total revenue surplus estimated in the year 2023-24 is of Rs 1,060 Crores. Chhattisgarh is among the progressive states which maintain a revenue surplus status.
- As a result of positive efforts made to increase the revenue of the state, State’s own tax revenue is estimated to be increase by 22% over that of 2023-24 (RE) to Rs 49,700 crore in 2024-25.
| Head | 2023-24 (Revised-RE) | 2024-25 (Estimate-BE) |
| Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) | Rs 5,05,887 Crore | Rs 5,61,736 Crore 11.0% higher than 2023-24 (RE) |
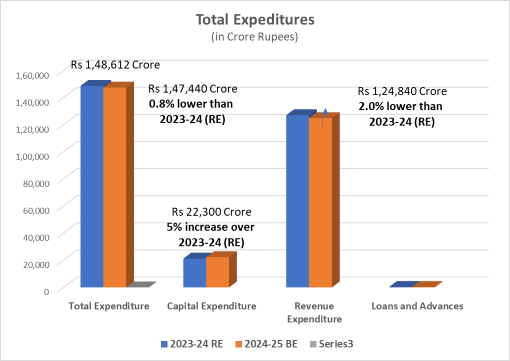
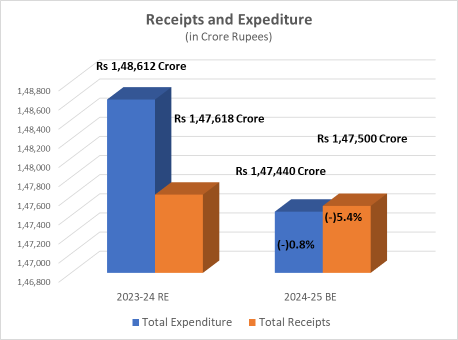
| Net Expenditure | Rs 1,48,612 Crore | Rs 1,47,440 Crore 0.8% lower than 2023-24 (RE) |
| Capital Expenditure | Rs 21,259 Crore | Rs 22,300 Crore 5.0% increase over 2023-24 (RE) |
| Revenue Expenditure | Rs 1,27,020 Crore | Rs 1,24,840 Crore 2.0% lower than 2023-24 (RE) |
| Loans and Advances | Rs 339.35 Crore | Rs 305.60 Crore 10.0% lower than 2023-24 (RE) |
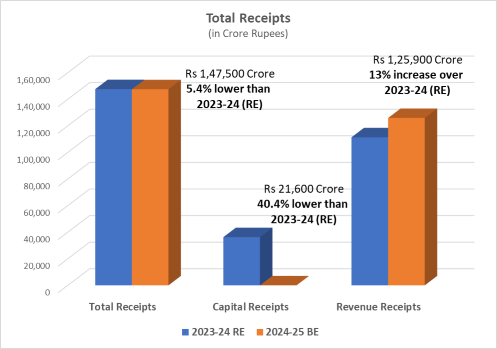
| Net Receipts | Rs 1,47,618 Crore | Rs 1,47,500 Crore 5.4% lower than 2023-24 (RE) |
| Capital Receipts | Rs 36,268 Crore | Rs 21,6000 Crore 40.4% lower than 2023-24 (RE) |
| Revenue Receipts | Rs 1,11,350 Crore | Rs 1,25,900 Crore 13% increase over 2023-24 (RE) |
| Revenue Balance (-) Deficit | (-) Rs 15,670 Crore (-) 3.1% of GSDP | (+) Rs 1,060 Crore (+) 0.2% of GSDP |
| Fiscal Balance (-) Deficit | (-) Rs 29,368 Crore (-) 5.81% of GSDP | (-) Rs 16,296 Crore (-) 2.90% of GSDP |
| Primary Balance (-) Deficit | (-) Rs 26,329 Crore (-) 5.2% of GSDP | (-) Rs 11,845 Crore (-) 2.1% of GSDP |
Source: Summary of the Budget 2024-25 | Main Budget 2024-25 | Press Note
Receipts

Revenue Receipts (राजस्व प्राप्तियाँ):
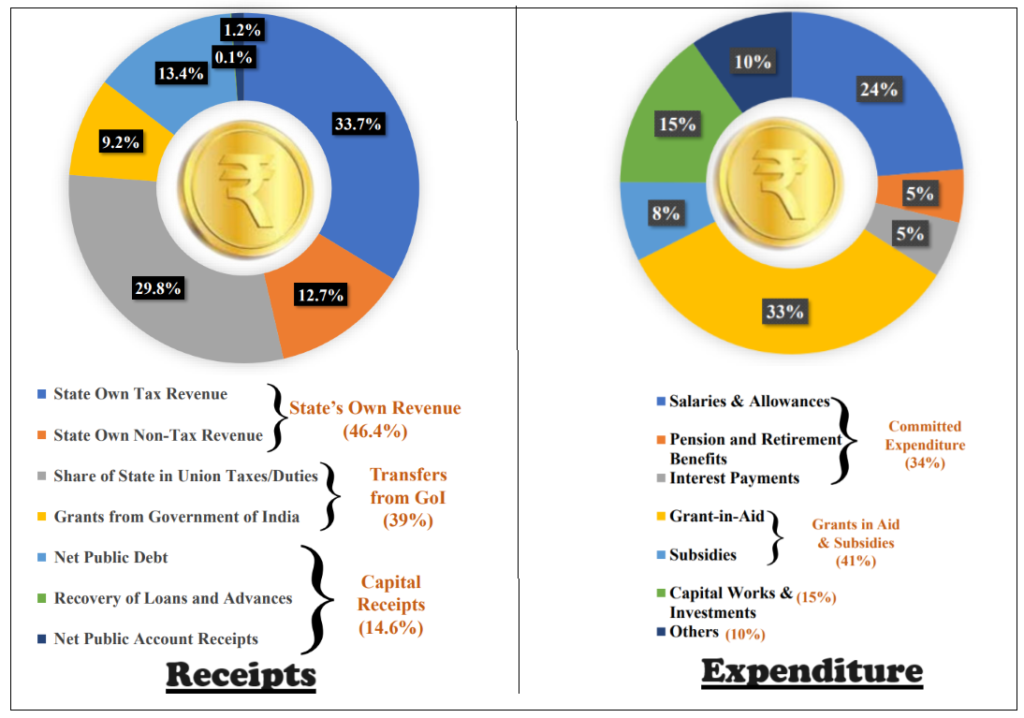
- The total revenue receipts for 2024-25 are estimated to be Rs 1,25,900 Crore (13% increase over 2023-24 (RE)). Of this, Rs 68,400 Crore (54% of the revenue receipts) will be raised through State’s own resources and Rs 57,500 Crore (46% of the revenue receipts) from central transfers, i.e. State’s share in central taxes (35%) and grants-in-aid (11%) from the central government. It is 9.8% increase over central transfers received in 2023-24 (RE).
- State’s own revenue: Rs 68,400 Crore (54% of the revenue receipts) will be raised through State’s own resources (12% of GSDP). State’s own tax revenue is estimated to be Rs 49,700 crore in 2024-25, an increase of 22% over that of 2023-24 (RE). Own tax revenue as a percentage of GSDP is estimated at 8.8% in 2024-25 which was 8% for 2023-24 (RE). State’s non-tax revenue is estimated to be Rs 18,700 Crore, an increase of 1.6% over that of 2023-24 (RE).
Capital Receipts (पूंजीगत प्राप्तियाँ):
- The main items of capital receipts public debt (लोक ऋण) is estimated to be Rs 19,750 Crore (39% lower than 2023-24 RE) which include market borrowings and from Banks, loans received from foreign governments.
- The total capital receipts for 2024-25 are estimated to be Rs 21,6000 Crore which is 40.4% lower than 2023-24 (RE)
- The receipts from public account include small savings (Post-Office Savings Accounts, National Savings Certificates, etc), provident funds and net receipts obtained from the sale of shares in Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs). They are estimated to be Rs 1,700 Crore in 2024-25 (54% lower than 2023-24 RE).
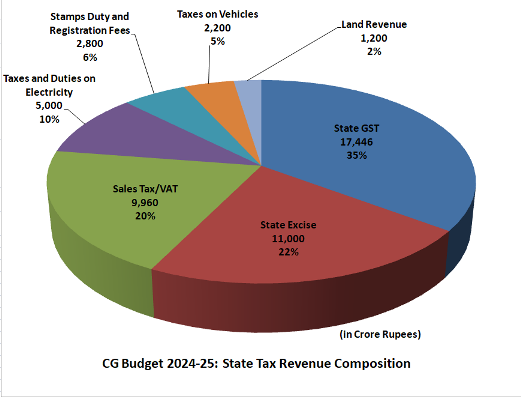
Tax Structure (Composition):
The major sources of State’s own tax revenue are:
| Head | 2023-24 (Revised-RE) | 2024-25 (Estimate-BE) |
| State GST | Rs 13,957 Crore | Rs 17,446 Crore 25.0% higher than 2023-24 (RE) |
| State Excise | Rs 8,500 Crore | Rs 11,000 Crore 29.0% higher than 2023-24 (RE) |
| Sales Tax/VAT | Rs 7,968 Crore | Rs 9,960 Crore 25.0% higher than 2023-24 (RE) |
| Taxes and Duties on Electricity | Rs 4,500 Crore | Rs 5,000 Crore 11.0% higher than 2023-24 (RE) |
| Stamps Duty and Registration Fees | Rs 2,500 Crore | Rs 2,800 Crore 12.0% higher than 2023-24 (RE) |
| Taxes on Vehicles | Rs 1,900 Crore | Rs 2,200 Crore 16.0% higher than 2023-24 (RE) |
| Land Revenue | Rs 1,200 Crore | Rs 1,200 Crore |
Expenditure
Capital Expenditure (पूंजीगत व्यय):
- Capital expenditure for 2024-25 is proposed to be Rs 22,300 Crore (5.0% increase over 2023-24 RE) which include expenditure affecting the assets and liabilities of the state, such as: (i) capital outlay, i.e. expenditure which leads to creation of assets (such as bridges and hospitals), and (ii) repayment and grant of loans by the state government.
- Debt Servicing (Debt Repayment) for 2024-25 constitutes about Rs 9,360 Crore (6.3% of Total Expenditure).
Revenue Expenditure (राजस्व व्यय):
- Revenue expenditure includes payment of salaries, pension, subsidies, grant and interest etc.
- Revenue expenditure for 2024-25 is proposed to be Rs 1,24,840 Crore (2.0% lower than 2023-24 RE)
- Debt Servicing (Interest Payments) for 2024-25 constitutes about Rs 7,851 Crore towards making interest payments (ब्याज भुगतान).
- Committed expenditure: Committed expenditure of a state typically includes expenditure on payment of salaries, pensions, and interest. In 2024-25, Chhattisgarh is estimated to spend Rs 50,624 crore on committed expenditure, which is 40% of estimated revenue receipts.
| Committed Expenditure | 2023-24 (Revised-RE) | 2024-25 (Estimate-BE) |
| Salari | Rs 30,401 Crore | Rs 34,956 Crore (28% of revenue receipts) |
| Pension | Rs 7,414 Crore | Rs 7,737 Crore (6% of revenue receipts) |
| Interest Payments | Rs 7,042 Crore | Rs 7,931 Crore (6% of revenue receipts) |
Loans and Advances (ऋण एवं अग्रिम):
- Loans and Advancers for 2024-25 is estimated to be Rs 305.60 Crore which is 10.0% lower than 2023-24 (RE.
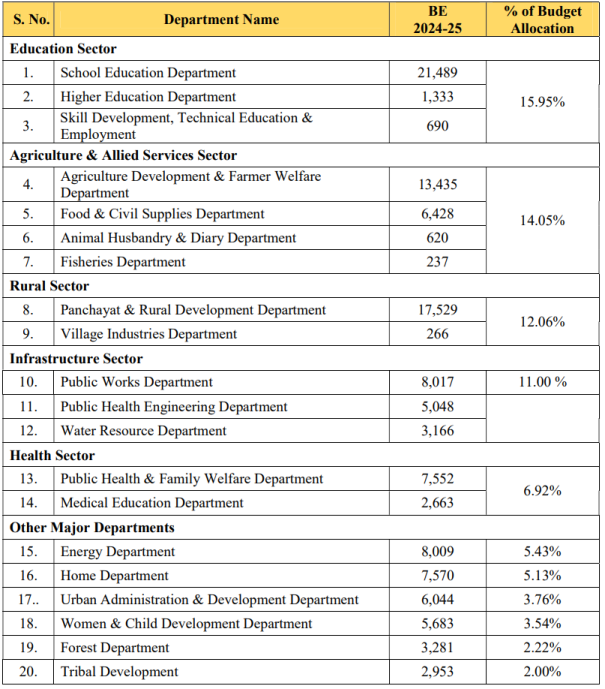
Sector-wise Budget Allocation
- The biggest increases in the departments’ budgets are in Women & Child Development Department (112% growth), Public Health Engineering Department (97% growth), Mineral Resources (80% growth) followed by Panchayat & Rural Development Department (70% growth) as compared to 2023-24 BE.
Receipts Vs Expenditure
Policy Highlights
This budget is dedicated to fulfil promises of “Modi ki Guarantee for Chhattisgarh” by
- Provision Rs 8,369 Crore for construction of 18 lakhs houses under Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana and Rs 3,799 Crore in 2nd Supplementary of FY 2023-24.
- Provision to empower women by assistance of Rs 12,000 per year under Mahtari Vandan Yojana.
- Provision of Rs 10,000 Crores under Krishak Unnati Yojana to benefit more than 24.72 lakh farmer which is an increase of 2.3 Lakh farmers from 22.4 Lakh farmers in the last year.
- Provision of Rs 4,500 Crores under Jal Jeevan Mission to expedite completion of works for ensuring tap water supply for all households.
- Provision for payment of Rs 5,500 per ‘manak boraa‘ for Tendupatta collectors up from Rs 4,000 per maanak boraa in last year.
- Provision of Rs 500 Crores under Deendayal Upadhyay Bhoomiheen Krishi Majdoor Yojana for annual payment of Rs 10,000 to landless labourers up from Rs 7,000 in last year.
- Provision for implementation of Chhattisgarh Uddyam Kranti Yojana for promoting self employment of youth.
- Provision for making detailed plan for the development of State Capital Region (SCR)
- Provision of Rs. 5 Crores for organizing Invest Chhattisgarh
- Provision of Rs. 5 Crores for making detailed plan for development of 5 Shakti Peeth of the state
- Provision of Rs. 35 Crores for Shree Ram Lalla Darshan for residents of the state.
15th Finance Commission’s Recommendations for 2021-26
The 15th Finance Commission’s (FC) report for the 2021-26 period was released on February 1, 2021. For the 2021-26 period, the Commission has recommended the share of states in the divisible pool of central taxes to be 41%. This is 1% point lower than the 42% share recommended by the 14thFC (for the 2015-20 period) to separately provide funds for the newly formed union territories of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh.
The 15th FC proposed revised criteria for determining the share of individual states (different from 14th FC). The Commission has prescribed certain conditions like transparency in accounts and improvement in property tax collections for availing these grants.
Based on the 15th FC’s recommendations for the period 2021-26, Chhattisgarh will have a 1.40% share in the divisible pool of central taxes. This implies that out of every Rs 100 of revenue in the divisible pool during the 2021-26 period, Chhattisgarh will receive Rs 1.40. This is higher than Rs 1.29 recommended by the 14th FC.
The 15th Finance Commission recommended the following fiscal deficit targets for states for the 2021-26 period (as a % of GSDP):
(i) 4% for 2021-22, (ii) 3.5% for 2022-23, and (iii) 3% for 2023-26.
As per the 15th FC recommendations, Chhattisgarh is expected to receive Rs 10,368 Crore as local body grants between 2021-2026. As of 2022-23, it has received Rs 4,791 Crore as local body grants. For 2023-24 (RE) and 2024-25, it is estimated to cumulatively receive Rs 3,511 Crore.
Public Debt Composition
Constitutional Provisions:
- Article 292: Government of India can borrow amounts specified by the Parliament from time to time.
- Article 293: State Governments in India can borrow only from internal sources.
Thus, the Government of India incurs both external and internal debt, while State Governments incur only internal debt.
Public Debt: Debt contracted against the guarantee of Consolidated Fund of India or State (defined as Public Debt)
- Internal debt: owed to lenders within the country.
- The government borrows by issuing the Government Bonds and T-Bills (Treasury Bills).
- Securities issued to International Financial Institutions
- Borrowing from RBI under Market Stabilization Scheme (MSS) Bonds for sterilization operations
- External debt: owed to creditors outside the country
- The outsider creditors can be foreign governments, International Financial
Institutions such as World Bank, Asian Development Bank etc., corporate and
foreign private households. - External debt may be of several kinds such as multilateral, bilateral, IMF loans, Trade
credits, External commercial borrowings etc. - When the non-resident Indians park their funds in India, it is also a type of external debt and
is called NRI deposits.
- The outsider creditors can be foreign governments, International Financial
Other Liabilities: Liabilities in the Public Account (called as Other Liabilities)
- Liabilities on account of Provident Funds
- Reserve Funds and Deposits, Other Accounts, etc
- Securities issued against ‘Small Savings’: All deposits under small savings schemes are credited to the National Small Savings Fund (NSSF). The balance in the NSSF (net of withdrawals) is invested in special Government securities.
Outstanding Liabilities:
Outstanding liabilities is the accumulation of total borrowings at the end of a financial year, it also includes any liabilities on Public Account. At the end of 2024-25, the outstanding liabilities are estimated to be 25.4% of GSDP, lower than the revised estimate for 2023-24 (25% of GSDP).

Economy of India and Chhattisgarh

 Home
Home Syllabus
Syllabus Contact Us
Contact Us